Business
Three ways to reimagine degree programs to increase equity, access, and job readiness

Published
4 years agoon

The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of higher education institutions.
Greater access to education could help reduce the disparities in educational attainment and increase employment opportunities that have been made worse by COVID-19.
Higher education institutions can use technology to make more degrees more accessible, design degree programs that are more hands-on and skill-based, and remove admissions barriers.
The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of higher education institutions worldwide. COVID-19 has contributed to the worsening of many young people’s employment prospects and pre-existing gender gap. In 2020, youth employment declined by 8.7%, more than twice that of adults 25-plus.
However, expanding access to education can open up economic opportunities. Higher education increases employment rates, job security, and lifetime earnings.
Students need access to skill-first learning opportunities to prepare them for the modern workplace in this uncertain and uneven economic environment. Higher education is more important than ever, including delivery, admissions, and curriculum. This will enable socioeconomic mobility by equitable access.
Higher education institutions need to leverage technology to reimagine degree programs to increase equity and access while also equipping students with the skills necessary to find work.
Use technology to get affordable and accessible degrees
The way universities deliver higher education has been revolutionized by advances in technology, especially online learning. Coursera’s enrollments doubled in 2020 and will increase by 32% in 2024. Online degree programs are being expanded by universities to reach students worldwide and meet growing demand.
Online learning technology allows students to access the best universities around the globe. Higher education institutions can also benefit from this. IIT Roorkee is a top-ranked institute in India and offers an online Post Graduate Certificate (in Data Science and Machine Learning) to its students. Over half (55%) of the students in this program are from outside India. The students come from 14 countries, including Canada and the United Kingdom. Their students come from more than 25% of the United States.
Universities can increase access by unbundling bachelor’s and master’s degrees to open online courses and stackable credentials. Universities can save money by using open content to attract students to online degrees at lower costs. Colombia’s Universidad de Los Andes has an online MSc in Software Engineering, which is 30% cheaper than the on-campus Master’s Degrees offered by Uniandes Engineering School.
Artificial intelligence (AI), a new avenue for universities, allows them to create programs on a large scale and reasonable price. Faculty and staff at the University of Michigan implemented auto graders to reduce time and improve lab management. Cloud infrastructure allowed the university also to minimize staff and DevOps expenses. AI technology can identify students who need one-on-one support to increase student outcomes.
For hands-on skill development, create job-relevant programs
Universities must adapt their programs to meet the demands of the rapidly changing labor market. Universities can use data-driven market research such as the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs report to identify the most in-demand degree programs based on job growth and align them with job outcomes.
Degree programs must provide students with the skills they need to succeed in the job market. More than 150 labs and assignments are available in the cloud at the University of Michigan’s Master of Applied Data Science. This includes more than 30-degree programs. Students can use a pre-configured Jupyter Notebook environment in-browser with real-world data sets, persistent storage, and high-computing capabilities.
To meet the demands of the global workforce, Queen Mary University of London recently launched an online Master of Science degree in Applied Data Analytics. The degree program prepares students to work in data science and data analytics roles. This is the top emerging job, according to the Forum. Students learn by doing real projects and building a portfolio.
Coursera data shows hands-on projects. Programming assignments can lead to a 30% higher rate of skill development and better career outcomes.
Eliminating admission barriers can increase equity and improve equity
Higher education institutions are eliminating application requirements to encourage a diverse student body.
Three online graduate programs at the University of Colorado Boulder offer performance-based admissions. Students are admitted to the University of Colorado Boulder’s online graduate programs by completing a performance pathway, a series of three-credit courses with a minimum 3.0 cumulative grade-point average (GPA). There are no applications, transcripts, fees, or entrance exams.
The university’s first online Master of Science degree in Electrical Engineering student didn’t hold a bachelor’s degree. He instead used five years of experience in the tech industry at top companies like Apple and Intel to complete the program in just one year. The university has seen a 30% increase in the number of admitted students to this program over the past year.
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign’s Gies College of Business removed the standard test requirements for several online degree programs to better serve underrepresented groups. The Online Master’s of Accounting (MSA), for example, saw a threefold increase in applications after removing the Graduate Management Admission Test(GMAT) requirement. Business schools typically use this test to evaluate the reading, writing, and analytical skills. In 2024, Coursera saw 73% growth in students from underrepresented programs.
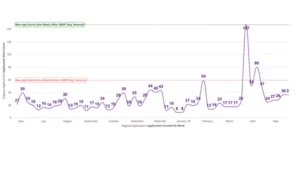
Applications for the Gies College of Business’s iMSA degree showing spike after removing GMAT requirement.
Many universities have created degree pathways that use industry-educated content. To prepare for entry-level IT jobs, learners can complete the Google IT Support Professional Certificate in just six months. The certificate can be stacked into a full-time degree, often required for managerial roles. The Google IT program was taken by 34% of current students in the University of London Bachelor of Science Computer Science in the United Kingdom. Many students continue to work even though they are pursuing their degrees.
This approach is promising in reaching underrepresented groups as 58% of US participants in the Google IT program identified themselves as veterans, women, Black, or Latinx.
These programs create highly qualified graduates who can work remotely and provide a diverse talent pool for global companies.
The global workforce faces unprecedented challenges due to rapid digital transformation and the COVID-19 crises. Higher education institutions can rethink the delivery of online degrees to ensure equal access for all people worldwide to affordable, work-relevant, and skills-first degrees.
Hi, my name is Nebojša, and I've been involved in digital marketing for over 15 years. I've written for various websites, covering a wide range of topics. I'm particularly interested in subjects like technology, gaming, app development, and I also have a passion for automobiles. Additionally, I work on SEO optimization. In my free time, I enjoy reading, walking, traveling and spending time with my wife and daughter.

You may like

In today’s rapidly shifting economic landscape, businesses often find themselves navigating uncharted waters. Financial control is more critical than ever, and for many organizations, the presence of an Interim Chief Financial Officer (CFO) can be a transformative catalyst.
These seasoned professionals bring a wealth of experience, ready to tackle the myriad challenges that arise when fiscal uncertainty looms large. An Interim CFO doesn’t just step in to fill a gap; they strategically reshape financial frameworks, implement robust controls, and establish rigorous reporting standards.
Whether it’s during times of transition, crisis management, or growth initiatives, their insights and expertise can mean the difference between stability and chaos. This article delves into the pivotal role Interim CFOs play in enhancing financial governance and ensuring that organizations emerge stronger from turbulent periods.
Assessing Financial Health

Source: bridgepointconsulting.com
Assessing financial health is a critical undertaking that interim CFOs approach with both rigor and insight. They dive deep into the numbers, examining everything from cash flow to profitability margins, understanding that each figure tells a story. This analysis goes beyond mere data; it weaves together trends, forecasts, and historical performance to create a comprehensive picture of the organization’s fiscal vitality.
Are there hidden costs lurking in operational expenses? Is revenue being maximized? These questions demand answers, and interim CFOs are adept at uncovering the nuances within financial statements. Their keen eye for detail allows them to identify both strengths and weaknesses within the financial framework, paving the way for strategic adjustments that can enhance both stability and growth.
In this dance of digits, agility is essential—because in the world of finance, timing can be everything.
Implementing Robust Financial Controls

Source: news24.com
Implementing robust financial controls is a critical step that interim CFOs take to fortify an organization\’s fiscal health. These controls serve as a safeguard, ensuring that financial processes are not only efficient but also transparent.
Picture a web of interconnected policies and procedures—document reviews, approval processes, and compliance checks—all woven together to minimize risk and prevent errors. An interim CFO often steps into a firm with fresh eyes, identifying gaps that may have eluded others for years.
They might introduce sophisticated auditing techniques while also streamlining simple tasks to foster a culture of accountability. By engaging teams in this process, they not only enhance accuracy but also empower staff to take ownership of their roles within the financial ecosystem.
In this intricate landscape, a strong framework of financial controls acts as both a compass and a shield, guiding decisions while protecting the organization from unforeseen pitfalls.
Enhancing Budgeting and Forecasting

Source: onboardingofficers.co.uk
Interim CFOs bring a fresh perspective to the often mundane world of budgeting and forecasting, transforming it into a dynamic tool for strategic insight. With their diverse experiences across industries, these financial leaders adeptly dissect existing budgets, uncoupling inefficient patterns and illuminating overlooked opportunities.
They introduce sophisticated modeling techniques that integrate historical data with real-time market trends, enabling organizations to anticipate shifts and respond with agility. Moreover, by fostering collaboration between departments, they craft a more inclusive budgeting process, one that aligns financial goals with operational realities.
The result? A robust financial roadmap that not only guides the present but also charts a course toward future growth, empowering businesses to navigate uncertainty with confidence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, interim CFOs play a pivotal role in enhancing financial control within organizations by bringing specialized expertise, fresh perspectives, and immediate operational efficiency. Their ability to swiftly assess financial systems, implement necessary changes, and provide strategic guidance allows companies, especially during transitional periods, to maintain stability and achieve their financial objectives.
Organizations looking to optimize their financial oversight should consider the strategic advantage of engaging interim CFOs to navigate complexities and foster growth. For more insights on leveraging financial expertise, visit www.fdcapital.co.uk to explore how interim solutions can elevate your businesss financial management.
Business
How to Cut Costs on Shipping to Amazon Warehouses – 2025 Update
Published
9 months agoon
June 16, 2025
Shipping products to Amazon FBA warehouses is a major expense for third-party sellers. Whether you’re shipping a single box via SPD (Small Parcel Delivery) or pallet loads through LTL/FTL (Less Than Truckload/Full Truckload), shipping costs can eat up 15% to 40% of your total margin if not carefully optimized.
In 2025, with higher fuel surcharges, regional delivery bottlenecks, and Amazon’s stricter FBA receiving policies, cutting shipping costs is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for profitability.
Checklist for Cutting Amazon FBA Shipping Costs
| Action | Benefit |
| Use Partnered Carriers | Save 30–70% on SPD/LTL rates |
| Consolidate into LTL when possible | Reduce per-unit cost and handling fees |
| Ship from prep centers near FCs | Shorten the last-mile distance |
| Use standard box/pallet dimensions | Avoid oversized penalties |
| Automate with FBA software tools | Reduce labor cost, avoid prep errors |
1. Choose the Right Shipping Method: SPD vs. LTL/FTL
Many sellers default to SPD because it’s familiar and easier to set up. But as your shipment volume grows, this method quickly becomes inefficient. If you’re sending multiple boxes regularly, switching to LTL or FTL can significantly lower your per-unit cost.
LTL is ideal for 1–4 pallets, while FTL becomes more economical once you’re shipping 20+ pallets. The larger and more frequent your shipments, the more you save through freight consolidation and pallet optimization.
| Shipping Method | Best For | Typical Volume | Cost Efficiency |
| SPD (Small Parcel) | Low-volume shipments (<150 lbs per box) | Under 10 boxes | Low to Moderate |
| LTL (Less Than Truckload) | Medium-volume shipments | 1–4 pallets | High for consolidated loads |
| FTL (Full Truckload) | Large shipments to one FC | 20+ pallets | Very high if volume allows |
Always run a side-by-side cost analysis between Amazon’s partnered LTL and SPD options for the same shipment. Even at lower volumes, LTL can beat SPD in cost-per-unit when handled correctly.
2. Optimize Box and Pallet Dimensions

Smartly stacked boxes and pallets in Amazon warehouses highlight how optimizing dimensions helps maximize space utilization
Dimensional weight pricing has become the standard for carriers, meaning your shipping bill depends as much on volume as on actual weight. Oversized packaging, under-filled boxes, or poorly stacked pallets all translate into wasted money.
Even minor changes to your box dimensions can cut down on shipping charges significantly. It’s especially important to standardize carton sizes across SKUs and ensure you’re getting the most efficient stackability when using LTL or FTL.
| Packaging Type | Cost Impact | Optimization Tip |
| Oversized Boxes | Higher per-unit cost + surcharges | Split items into smaller boxes |
| Inconsistent Sizes | Inefficient pallet use | Use standard cartons |
| Poor Pallet Stacking | May result in Amazon rejections | Follow Amazon’s FBA pallet guidelines |
A Freightos shipping case study found that by trimming box height by just 2 inches across 300 monthly units, one seller saved $420 in dimensional weight charges over 30 days.
3. Consolidate Shipments Strategically
Frequent small shipments often result in higher per-unit shipping costs, more carrier pickups, and a higher likelihood of fulfillment center delays. Consolidating multiple small shipments into a single, well-organized load saves on handling and often qualifies for better freight rates.
More importantly, Amazon prefers well-labeled, bulk deliveries over fragmented ones, which can
delay check-ins during peak seasons.
| Scenario | Estimated Monthly Shipping Cost | With Consolidation |
| 4 SPD shipments × 10 boxes | $900 | $540 |
| 1 LTL pallet shipment (same qty) | — | $480 |
If you’re using a prep center or 3PL, schedule shipments biweekly or monthly instead of weekly. Many centers will hold goods for a few extra days to help you consolidate at no added cost.
4. Use a Prep Center Near Amazon FCs

A prep center near Amazon warehouses ensures faster and more accurate processing of shipments ready for dispatch
Shipping across the country adds avoidable costs, especially if your inventory is already located closer to Amazon’s main fulfillment hubs, according to Dollan Prep Center. Working with a prep center within a short distance of Amazon’s major FCs helps you reduce last-mile freight charges, shorten delivery windows, and reduce potential delays during appointment scheduling.
This also increases the chances of faster check-ins and fewer rescheduling penalties.
| Top FC Regions | Benefits of Nearby Prep Centers |
| Dallas/Fort Worth, TX | Central location, multiple nearby Amazon FCs |
| Hebron, KY | Common FBA inbound point for East Coast sellers |
| Moreno Valley, CA | Ideal for West Coast imports from Asia |
| Allentown, PA | High Amazon FC density, fast East Coast distribution |
Relocating your prep and storage from the West Coast to Kentucky or Ohio can reduce per-pallet shipping costs by 20–30%, especially for sellers distributing nationwide.
5. Leverage Amazon’s Partnered Carrier Program
Amazon offers discounted rates through its partnered carrier program, which includes both UPS for SPD shipments and several freight providers for LTL and FTL loads. These discounts are only available if you create shipments directly through Seller Central and use Amazon’s pre-approved carriers.
In most cases, Amazon’s partnered rates beat outside quotes, even those from negotiated commercial accounts.
| Service | Estimated Discount |
| Partnered SPD (UPS) | 30%–50% |
| Partnered LTL (XPO, CEVA, etc.) | 40%–70% |
While you must comply with Amazon’s strict packaging and labeling requirements to access these rates, the savings are substantial, l—especially for high-volume sellers or those regularly shipping to distant FCs.
6. Reduce Rejected Shipments with Better Labeling and Packing

Neatly stacked boxes in Amazon warehouses demonstrate strategies to reduce rejected shipments and improve delivery efficiency
FBA rejections are costly and often entirely avoidable. If your shipment arrives with incorrect labels, mixed SKUs, damaged boxes, or non-standard pallets, Amazon may either reject the shipment or charge you additional fees for correction.
These mistakes lead to delays, inventory miscounts, and wasted freight costs. Proper prep practices—including double-checking barcode placements and securely packing all cartons—go a long way in avoiding financial hits.
| Mistake | Possible Charge |
| Wrong label placement | $0.20–$0.30 per unit |
| Unscannable barcode | $0.15–$0.40 per unit |
| Rejected pallet | Full reshipment cost |
Based on Amazon seller reports, approximately 1 in 5 shipments that result in receiving delays are traced back to labeling or prep errors, ot transport problems.
7. Compare 3PL and Freight Forwarder Rates
Freight pricing varies widely depending on your route, volume, and carrier network. Many sellers overlook potential savings by sticking with default options like Amazon Partnered LTL when they could secure lower rates via third-party logistics (3PL) providers or freight brokers.
For international shipments, especially from Asia, consider FBA-friendly freight forwarders who understand Amazon labeling and delivery protocols.
| Shipping Scenario | Amazon Partnered Rate | 3PL Broker Rate | Savings Potential |
| 3 pallets to California FC | $620 | $520 | ~$100 (16%) |
| Full container from China | $2,400 | $1,800 | ~$600 (25%) |
Always confirm that your 3PL or freight broker can handle Amazon’s strict delivery appointments and ASN documentation. Mishandled deliveries can delay check-in by days or even weeks.
8. Use Software to Automate and Optimize Shipping
Managing logistics manually might work at a small scale, but as your operation grows, automation is critical. FBA-compatible software can help you generate labels, track freight costs, schedule restocks, and reduce prep errors.
Most tools also offer data dashboards that allow you to compare historical shipping costs and identify which products are the most expensive to move.
| Tool | Functionality |
| InventoryLab | Shipment creation, cost tracking, and label printing |
| RestockPro | Restocking suggestions and forecasting |
| ShipStation | Multi-carrier shipping rate comparisons |
| Sellerboard | Profit analysis, including logistics cost modeling |
Automating shipment creation and integrating freight cost visibility into your inventory management can help reduce administrative time by 20–30% and prevent avoidable prep center errors.
9. Negotiate Better Terms with Your Prep or Freight Providers
Shipping costs are not always fixed. If you’re consistently sending volume to FBA, you have leverage. Many prep centers, LTL brokers, and freight forwarders offer volume discounts, flat fees per pallet, or reduced storage costs if you ask.
Review your past 3–6 months of shipping data, calculate your average pallet count, and initiate a negotiation with your vendors.
Tip: Sellers averaging 10+ pallets per month can often secure flat monthly pallet rates, discounted receiving, or free shrink-wrapping—terms that reduce your cost per unit long term.
10. Eliminate Dead Weight: Audit Unprofitable Shipments

A focus on eliminating dead weight in Amazon warehouses leads to lighter, more cost-effective shipments
Not every product is worth shipping. It’s easy to fall into the trap of sending every piece of inventory to FBA, regardless of sales velocity or margin. Always review your SKU profitability before creating a shipment.
If a product yields less than $5 net profit after shipping and FBA fees, it may not be worth warehousing, especially if it ties up cash flow or increases long-term storage fees.
Sellers who regularly audit their shipping loads and purge underperforming inventory can reduce overall FBA shipping costs by 15–25%, according to Helium 10 seller data from Q4 2024.
Conclusion
Shipping costs are one of the easiest areas to improve once you understand the variables that impact pricing, from carton sizes to shipping method selection, from software automation to vendor negotiation.
In 2025, sellers who optimize these components can see thousands in annual savings and increase their margins without selling a single extra unit. Whether you’re operating at 500 units per month or 50,000, controlling your logistics pipeline will separate your business from competitors who let costs run unchecked.
Business
Post-Purchase Customer Experience – Why It’s the Key to Retention and Loyalty
Published
1 year agoon
February 6, 2025
In today’s fiercely competitive marketplace, securing a sale is just the beginning of the customer journey, not the end. Post-purchase customer experience has emerged as a pivotal aspect of not only retaining clients but also building unwavering loyalty.
Once the transaction is completed, a new chapter unfolds—one that can either transform a one-time buyer into a lifelong advocate or reduce them to just another statistic in the sea of disengaged consumers. Every interaction a customer has after the purchase, from personalized follow-ups to seamless customer support, plays a crucial role in shaping their perception of your brand.
As the dust settles on their initial decision to buy, it’s the ongoing experiences that will ultimately determine whether they return for more or drift away into the clutches of competitors. Understanding and optimizing this journey is not merely an option anymore; it’s a necessity for businesses striving to cultivate lasting relationships in a world where choices abound.
The Path to Loyalty: How Post-Purchase Experience Shapes Customer Relationships

Source: reverselogix.com
The journey to fostering customer loyalty begins long after the initial purchase is made; it is intricately woven into the fabric of the post-purchase experience. Picture this: a customer who eagerly anticipates their delivery, receiving a thoughtful follow-up email that not only confirms shipment but also includes tips for maximizing the product’s use—this simple gesture cultivates a sense of connection.
Afterward, a timely survey asking for feedback demonstrates that their voice matters, transforming a transactional relationship into a dialogue. Each element, from personalized recommendations based on their purchase history to dedicated customer support, deepens trust and enhances the emotional bond.
In this ever-competitive landscape, understanding that retention hinges not on the initial sale, but on the entire journey afterwards, can unlock the secret to creating lifelong advocates for your brand.
Beyond the Sale: The Critical Role of Aftercare in Customer Retention

Source: globalresponse.com
In the whirlwind of commerce, where transactions often take center stage, one critical aspect frequently slips through the cracks: aftercare. This pivotal phase begins the moment a customer clicks “confirm” on their order, extending well beyond the point of sale.
It’s not merely a follow-up; it’s a commitment to nurturing the relationship, a chance to reinforce the connection established during their buying journey. Think of aftercare as the secret sauce of customer loyalty—personalized messages, helpful tips, and timely support can transform an ordinary experience into an extraordinary one.
Customers who feel valued and supported are more likely to return, not just for the products they cherish but for the community and service that accompany them. In a landscape flooded with choices, businesses that prioritize aftercare don’t just sell products; they cultivate loyalty, turning one-time buyers into lifelong advocates.
Conclusion

Source: youngurbanproject.com
In conclusion, the post-purchase customer experience is a critical pillar in fostering retention and loyalty among consumers. By understanding and enhancing this stage of the customer journey, businesses can build lasting relationships that go beyond a single transaction.
Effective post-purchase marketing not only reinforces the value of the initial purchase but also encourages repeat business through personalized communication and ongoing engagement. As companies strive to differentiate themselves in a competitive landscape, prioritizing the post-purchase experience will prove essential in transforming customers into brand advocates, ultimately driving sustainable growth and long-term success.
Order Tracking Experience Optimization For DTC Brands

How Much Money A Travel Agent Can Earn Today

High End Business Dinner Venues In Munich City Center

Game On: North Texas is a ‘Technology Entertainment Concept ‘Paradise.

Cannondale Information: All-new Topstone Carbon gravel bicycle unveiled.

EU takes steps to legislate sustainable fashion. It will work.
Trending
-

 Entertainment4 years ago
Entertainment4 years agoGame On: North Texas is a ‘Technology Entertainment Concept ‘Paradise.
-

 Sports4 years ago
Sports4 years agoCannondale Information: All-new Topstone Carbon gravel bicycle unveiled.
-

 Fashion4 years ago
Fashion4 years agoEU takes steps to legislate sustainable fashion. It will work.
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoCustomer Experience Innovation: The New Battlefield For Businesses.
-

 Fashion4 years ago
Fashion4 years agoDubai Design District welcomes leading Polish designers to the world-class fashion community.
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoThe Defence industry supports hundreds of UK jobs and business.
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoWhat is Nudekay, and How can I create it?
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoA Guide To Anti-Money Laundering For Your Business.